Microbiology department
The Microbiology Department in a laboratory is responsible for identifying and characterizing microorganisms that cause infections in patients. Here’s an overview of what you might find in a typical Microbiology Department within a laboratory:
Culture and Sensitivity Testing: One of the primary functions of the Microbiology Department is to culture and identify bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites from patient samples such as blood, urine, sputum, wound swabs, and other body fluids. Once identified, these microorganisms are subjected to sensitivity testing to determine the most effective antimicrobial agents for treatment.
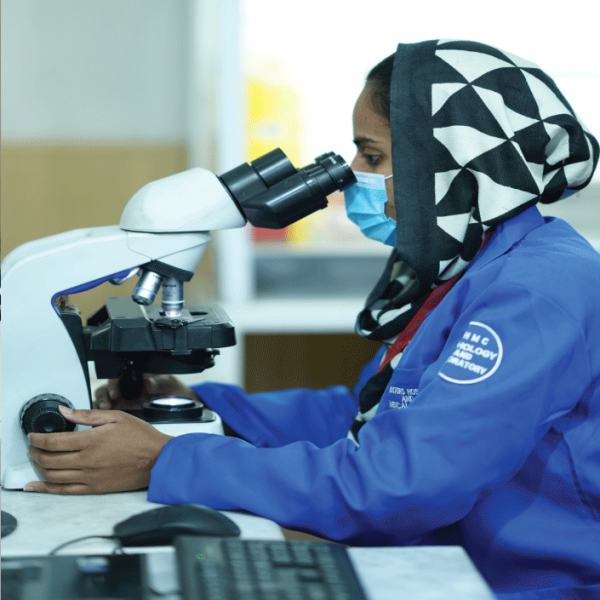
Microscopy: Microscopy techniques, including Gram staining, acid-fast staining, and direct examination under the microscope, are used to visualize microorganisms and provide preliminary information about their characteristics and potential pathogens.
Automated Systems: DHMC laboratories utilize automated systems for rapid identification and susceptibility testing of microorganisms. These systems can significantly reduce turnaround time and improve the efficiency of microbiological testing.

Molecular Diagnostics: Molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), and DNA sequencing are used for the rapid and accurate identification of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. These techniques are especially valuable for detecting pathogens with fastidious growth requirements or those that are difficult to culture.
Epidemiological Surveillance: Microbiology laboratories participate in surveillance programs to monitor the prevalence of nosocomial infections, identify outbreaks, and track antimicrobial resistance patterns within the hospital or community. This information is critical for implementing infection control measures and guiding treatment protocols.
Quality Control and Assurance: Rigorous quality control measures are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of microbiological test results. This includes regular calibration of equipment, proficiency testing, and adherence to standardized protocols and procedures.
Safety Protocols: Microbiology laboratories adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent the spread of infectious agents and protect laboratory staff. This includes the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), biological safety cabinets, and proper disinfection and sterilization procedures.
Research and Development: DHMC microbiology laboratories engage in research and development activities to improve diagnostic techniques, develop new assays for emerging pathogens, and contribute to the scientific understanding of infectious diseases.
Overall, the Microbiology Department in a laboratory plays a critical role in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of infectious diseases, contributing to patient care and public health efforts.